As the global conversation on climate change intensifies, so does the urgency to understand its multifaceted effects on various sectors. In particular, Australia’s solar energy landscape, is influenced by climatic shifts, technological advancements, policy dynamics, and socioeconomic factors. We’re going to take a look at the relationship between climate change and solar energy consumption in Australia, exploring how climate change has impacted this industry so far and how it may continue to do so in the future.
Solar in Australia
2013-2017 was the hottest five-year period on record, and July 2023 was the hottest month humanity has ever experienced. All an impact of man-made climate change and largely our dependency on fossil fuel energy consumption.
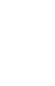
“Australia’s electricity sector is the nation’s single largest source of greenhouse gas pollution – accounting around a third of total greenhouse gas emissions.” (source)
Fossil fuels contributed 71% of total electricity generation in 2021, including coal (51%), gas (18%) and oil (2%).
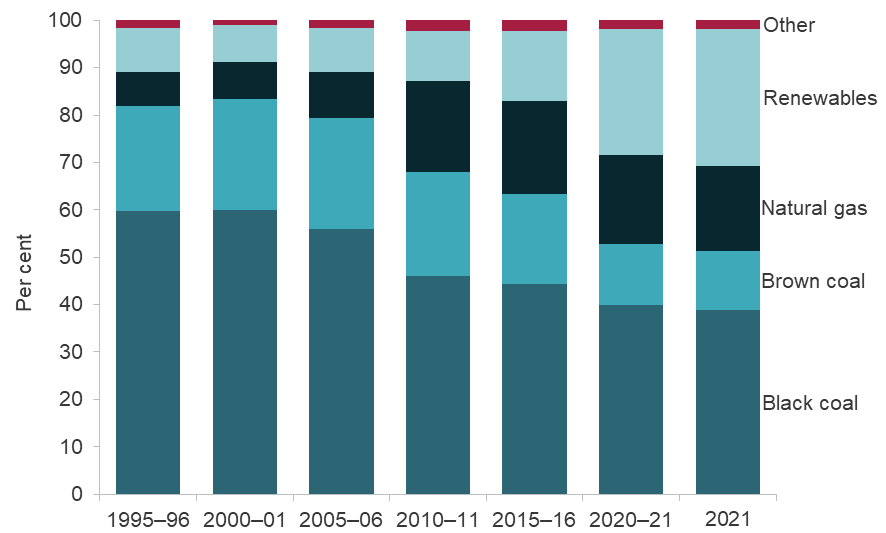
Over the past few decades, Australia’s embrace of solar power has been marked by both accomplishments and hurdles. But the linear trend line is one of strong growth in solar energy demand and production.
The graph below represents the growth of renewable energy supply up to 2021.
“Stabilising the climate at livable levels requires the vast majority of the world’s fossil fuel reserves to be left in the ground, unburned. Globally, about 88% of the coal reserves must not be mined (McGlade and Ekins 2015).”
Call us Get a solar quote for your business
How climate change has positively affected solar energy
Grid-connected solar power systems – sometimes called large-scale photovoltaics (PV) – are Australia’s fastest-growing renewable energy technology. (source)
A combination of increased education around the impacts of climate change, and the fossil-fuel-related cause behind it, increased electricity costs, as well as improved technological advances and decreased costs in supply, has led to a solar energy industry that has absolutely boomed in the last decade.
“Hundreds of thousands of Australian households have benefited with solar PV panel prices falling 75% in the last 5 years.” source
“Tackling climate change requires substantial and sustained reductions of carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions and decarbonising the Australian economy. Burning fossil fuels for electricity production is the largest source of greenhouse gas emissions driving climate change. In fact, electricity and heat production represent a quarter of global greenhouse gas emissions (IPCC 2014).”
The benefits are substantial and diversifying our energy portfolio is essential to reduce our greenhouse gas emissions and work towards net-zero emissions for the future of our species.
How climate change will negatively impact solar energy
Climate projections indicate that Australia will experience more ‘solar ramps’. These are sudden variabilities in climate, such as cloud cover, seasonal cycles, etc. Climate change will make solar ramps more frequent and longer lasting, affecting solar energy system performance.
Therefore, the best scenario for Australia would be a combination of battery storage and varied renewable energy sectors, including wind and hydro to reduce sole reliance on solar energy and create reliable energy networks.
“Australia is the sunniest country in the world and one of the windiest; it has enough renewable energy resources to power the country 500 times over.” source
If you’re interested in solar energy for your business, we can help. We install smaller systems, eligible for STCs and larger systems 100kW+ that are eligible for LGCs.
Call us Get a solar quote for your business